A first version of this article was first published in Spanish on LinkedIn
With the increasing adoption of emerging technologies such as Web3, Blockchain, Smart Contracts and Cryptocurrency, the concept of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), is gaining considerable attention. DeFi radically changes the way we use financial instruments.
While the traditional financial system works on a centralized platform, controlled by government agencies and intermediaries of all kinds, DeFi works according to a protocol that runs on a decentralized infrastructure powered by Blockchain (mainly Ethereum). Consequently, programmers can develop customized, efficient and secure financial platforms that are open to anyone with access to a computer and internet connection.
Undoubtedly, DeFi is the new frontier, since it allows millions of people who do not have access to traditional financial systems (for various reasons, globally more than 1,700 million people are unbanked), to be the managers of their finances and transact with everyone – thanks to decentralization, promoting equal opportunities and unprecedented economic growth.
The infrastructure of DeFi is composed of:
Blockchain – The backbone for DeFi operations is a Blockchain that allows transactions with shared data and under various pre-established assumptions. This data is packaged in “blocks” and cryptographically “chained” allowing an audit of the transaction history. Blockchains are possible due to a “Consensus Protocol”, a set of rules that determine the types of blocks that can be part of the chain and become the “truth”. Blockchains generally use a “Proof of Work” consensus protocol, or alternative mechanisms such as the “Proof of Stake”.
Cryptocurrencies – The most popular application of Blockchain is Cryptocurrency, which is a (normally scarce) token that is secured, quoted and transferred cryptographically (“taking into account that digital objects are easily copyable”). It is this scarcity that guarantees its value; Cryptocurrencies are themselves a Blockchain innovation. As Eric Schmidt, former CEO of Google, has said “Bitcoin is a remarkable cryptographic achievement, since the ability to create something that is not duplicable in the digital world, has enormous value”.
The pioneering model of cryptocurrency is Bitcoin, whose protocol works almost exclusively as a payment network, with the ability to store and perform financial transactions around the world and in real time, without intermediaries, institutions and control systems. This powerful value proposition gives Bitcoin its high market value (as of 6 December 2021, one Bitcoin costs US$50,403.51, with a market capitalization of US$952.7 billion). Although the Bitcoin network is very strong, its technological competitors offer greater functionalities (such is the case of the Ethereum Blockchain that has Ether as its cryptocurrency and main asset, with a cost of US$4,341.85 and a market capitalization of US$513.7 billion. Ethereum offers a wide range of opportunities to power DeFi and in general the decentralized internet Web 3.0).
According to visionary Sandeep Nailwal, co-founder of Polygon (a firm specialized in building protocols that connect Blockchain networks compatible with Ethereum), between 60% or 70% of the crypto industry currently works on the Ethereum network. So, will this mean that Web 3.0 will be built on top of the Blockchain of the second cryptocurrency by market cap?
Market quote of the main Cryptocurrencies
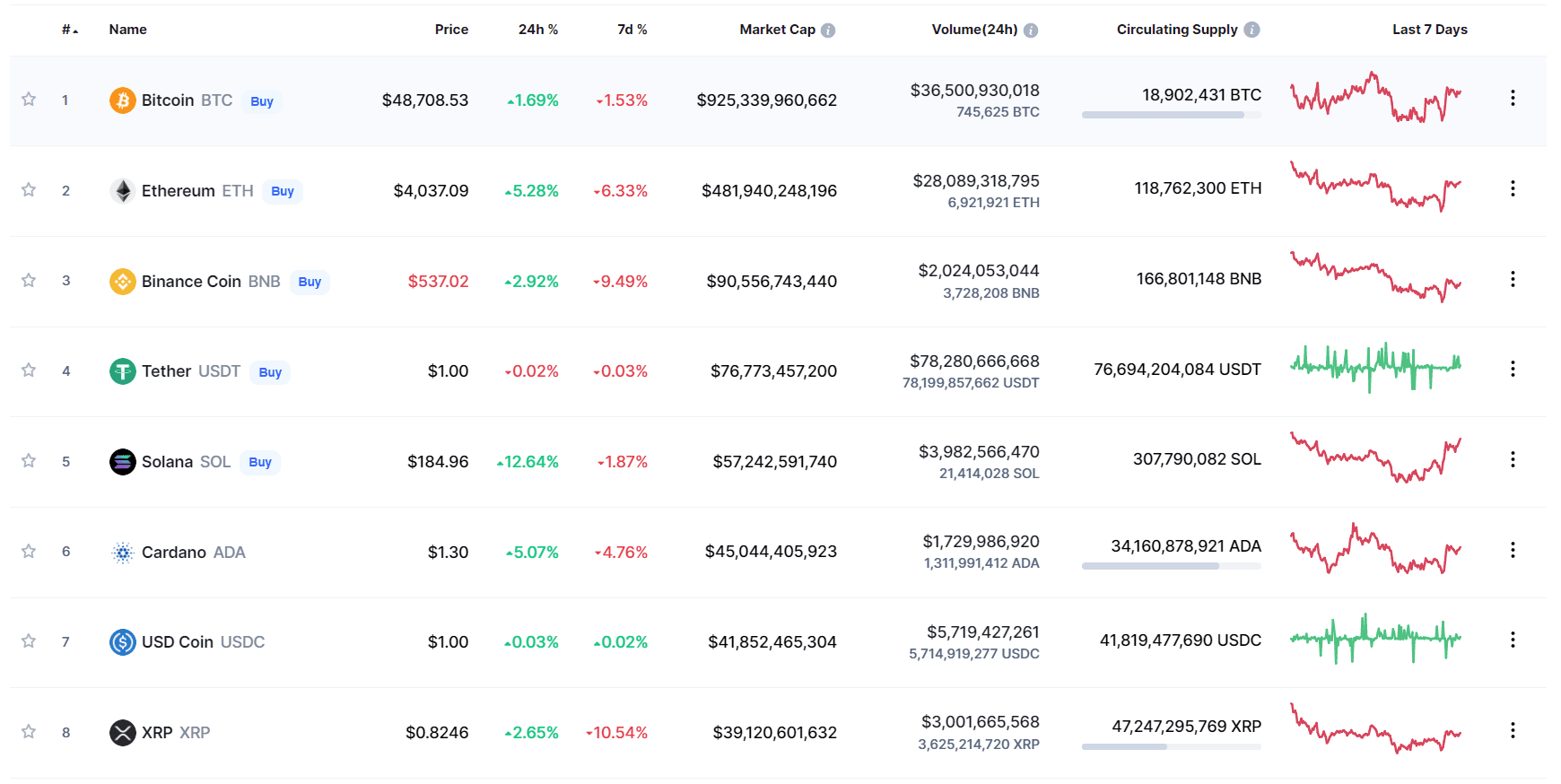
(source coinmarketcap.com)
Smart Contracts – A crucial component of DeFi, it is a Smart Contracts platform. These platforms go beyond a simple payment network (such as Bitcoin) and allow the creation of rules for any type of transaction and can even create scarce assets with specialized functionalities. Many of the clauses of traditional commercial agreements could be transferred to a smart contract, which would not only list, but algorithmically apply these clauses (putting in check a whole series of entities that currently endorse transactions manually, such as: notaries, property registrars, lawyers who certify public procedures and other such actors).
Smart Contracts go beyond finance and have applications as diverse as video games, such as the famous Axie Infinity or the incredible Decentraland, which allows you to create, explore and trade in a virtual world (Metaverse).

Other applications of Smart Contracts are in data management, a supply chain with a powerful IoT, electoral processes, claims to insurers, traceability of merchandise in containers worldwide, copyright and intellectual property protection, and many others.
Oracles – One problem with Blockchain protocols is that they are isolated from the world outside the chain itself. For example, the Ethereum Blockchain only knows with authority what is happening in its own network, and not in other networks or protocols, restricting the applications of Smart Contracts and native Ethereum Tokens, thus reducing the usefulness of the platform. This is known as the Oracle Problem.
In the context of Smart Contracts, an Oracle is any source of data to report information external to the original Blockchain and represents a huge challenge for DeFi to achieve utility beyond its isolated chain. A clear example of this is the Chainlink Blockchain Oracles for Hybrid Smart Contracts platform, designed on Ethereum, aiming to solve the problem of communication outside the original Blockchain.
Stablecoins “the place where traditional finance and DeFi meet” – A major shortcoming of many cryptocurrencies is the excessive volatility of their market quotes. This can cause friction in users of DeFi applications, due to the low risk tolerance of a volatile asset such as Bitcoin, Ether or another cryptocurrency. To solve this, an entire subclass of Cryptocurrencies called Stablecoins has emerged, which maintain a price parity with some reference asset, such as the US Dollar, the Euro, the Pound Sterling, Gold, etc. This parity provides stability to investors in the use of DeFi applications and they can even be used to provide market exposure in the performance chain of an asset that is outside the Blockchain, for example: gold, shares of companies or ETFs (Exchange-traded Fund such as the VOO – Vanguard that is indexed to the S&P500).
The three main types of Stablecoins are: (1) Fiat-guaranteed, (2) crypto-guaranteed, and (3) un-collateraled. The largest fiat-guaranteed Stablecoin is Tether (USDT), with a market capitalization of US$75.6 billion – making it the fourth largest cryptocurrency today behind Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH) and Binance Coin (BNB).
The second largest Stablecoin is USD Coin (USDC), backed by Coinbase. Both Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) are very popular and useful for integrating into DeFi protocols.
Decentralized Applications – dApps are a fundamental component of DeFi. These software applications are similar to traditional ones, except that they work on Smart Contracts platforms. The main advantages are the absence of permits and the independence with which they operate (without the intervention of control entities). dApps can be developed/used by anyone with a computer and internet access.
Without a doubt, right now Ethereum is the “programmable Blockchain of the world”. The internet that we know, Web 2.0, will change radically with the entry of Web 3, and of course it will change the way we live (Metaverse).
Some DeFi products or applications
While we are in the early stages of these technologies; Blockchain, DeFi and Smart Contracts are creating new opportunities at an incredible speed. For example:
- Credit and mortgage management platforms using cryptocurrencies as collateral, promoting that interest rates are regulated by the market itself, instead of centralized entities such as: Governments, the Federal Reserve or Central Banks. Of course, there are many risks such as money laundering and /or tax schemes that promote evasion, so governments are actively working on developing regulatory projects based for example on Artificial Intelligence, IoT or other exponential technologies.
- Financing of infrastructure projects, real estate, technology, sustainability and climate change, etc.; through the use of Tokens and Smart Contracts. Anyone can be an investor in large-scale global projects, financed through DeFi instruments.
- Companies that list their shares on traditional systems such as NYSE, London Stock Exchange, Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE/TYO) or BOVESPA. They will begin to issue tokens “a kind of shares in shares” that can be acquired in a decentralized way by users around the world, giving the opportunity to access the stock market to a large number of investors of all sizes.
- Large Decentralized Marketplaces, where interested parties can exchange goods or services. So, we have the incredible market of NFTs (Non Fungible Tokens) and the great opportunities that this has for the Orange Economy. For example, Open Sea, the largest NFT Marketplace in the world, the Crypto Punks Larva Labs market or the BAYC – BoredApeYatchClub, where Adidas made its entrance to the Metaverse using figures from the famous Apes.
- Other financial and investment products we do not yet know – futures market, means of payment, investments in digital assets of all kinds, investments in the Metaverse, etc.
Conclusion
DeFi is in clear exponential growth. However, it remains immature and volatile, with a number of economic, technical, ethical and public policy issues that need to be addressed. DeFi has the potential to transform global finance, but activity to date has focused on speculation, leverage and generating returns among the community of digital asset owners. Ultimately, DeFi’s success or failure will depend on whether it can deliver on its promise of open-to-all, high-trust, and unguarded (guarded) financial services.
| Traditional | Fintech | DeFi | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Issuing money | The State | Proof of work and Proof of Satake rewards | |
| Transferring money | Cash | Revolt,Transferwise | Cryptocurrency and token transaction |
| Lending/borrowing Money | Banks | Lending Club | Tokenized P2P debut |
| Exchange assets | Exchange& Brokers, like Nasdaq | Decentralized exchange | |
| Investing money | Stocks, Bonds, etc, accessible though banks and exchange | Robinhood | Tokenized financial products (ICOs, STOs and Token baskets) |
Local Knowledge – International Coverage
Founded in 1979, Auxadi is a family-owned business working for multinational corporations, private equity funds and real estate funds. It’s the leading firm in international accounting, tax compliance and payroll services management connecting Europe and the Americas with the rest of the world, offering services in 50 countries. Its client list includes many of the top 100 PERE companies. Headquartered in Madrid, with offices in US and further 22 international subsidiaries, Auxadi serves 1,500+ SPVs across 50 jurisdictions.
All information contained in this publication is up to date on 2021. This content has been prepared for general guidance on matters of interest only, and does not constitute professional advice. You should not act upon the information contained in this chart without obtaining specific professional advice. No representation or warranty (express or implied) is given as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in this content, and, to the extent permitted by law, AUXADI does not accept or assume any liability, responsibility or duty of care for any consequences of you or anyone else acting, or refraining to act, in reliance on the information contained in this chart or for any decision based on it.




