Technology for visibility and oversight
Financial situations can change rapidly and you need up-to-date information to be able to properly strategise. You need to be able to access your data quickly while keeping control of payment and payroll approvals. The importance of data access and control increases tenfold when you have data from multiple locations.
When expanding into a new country, there are options to manage your financial data, accounting, tax compliance and payroll requirements. Here, we take a brief look at the pros and cons.
Local recruitment – hiring staff in the new location to supplement your current team
- They’ll be on the ground in the new location, should know the local regulations and be able to guide you through HR compliance and tax issues.
- They may also be able to manage local payroll and registrations, and ensure local tax compliance.
- You’ll be able to access real-time data and maintain visibility and control.
- Time zones may affect the smooth operation of your finance and HR teams.
- Direct oversight may be difficult and skill levels / management might not be at the same standard as in the headquarter country.
- You’ll need to have desk space for the staff, possibly boosting your real estate requirements, and your systems strength will need to be able to manage remote working (though data access may be poor or limited in certain locations).
- You’ll have to train them on your systems, which means initial downtime – the benefits of more staff aren’t immediately felt.
- You may possibly even have to upgrade your IT systems to be able to manage the large volumes of data they’ll need to access.
Outsource to a third-party provider
Investigations will be required to ensure you’re getting the most from the provider, so you should think about everything you’ll need (accounting, reporting, tax compliance, and payroll management at the least). Take the time to research available providers and meet with them. Can the provider do everything you need them to?
- No financial outlay for staff or IT systems and no training downtime.
- No need to hire, train or provide desk space – as a third-party provider, they’ll operate independently.
- No need for your finance or HR teams to learn new labour codes or tax laws – the provider will have all the knowledge you need.
- No need to worry about your local accounting or reporting, except final checks.
- For future growth, your provider should be able to grow with you, providing services in locations as and when you need; no need for local recruitment.
- Your provider will often make the investment in relevant technology you need, so that you don’t have to.
- No access to real-time data; you’ll probably have to ask and then wait for a response (which may also be affected by time zones). You won’t have full control of your data, and you won’t have full visibility. Careful monitoring will be required.
- The reporting produced may not match your own – data consolidation and consolidated reporting may be complicated.
- Time zones may affect the smooth operation of your teams.
- Data security may be a concern.
- No direct oversight.
- You may be dealing with several people on your account, possibly leading to communication issues.

Outsource to a professional partner – like Auxadi
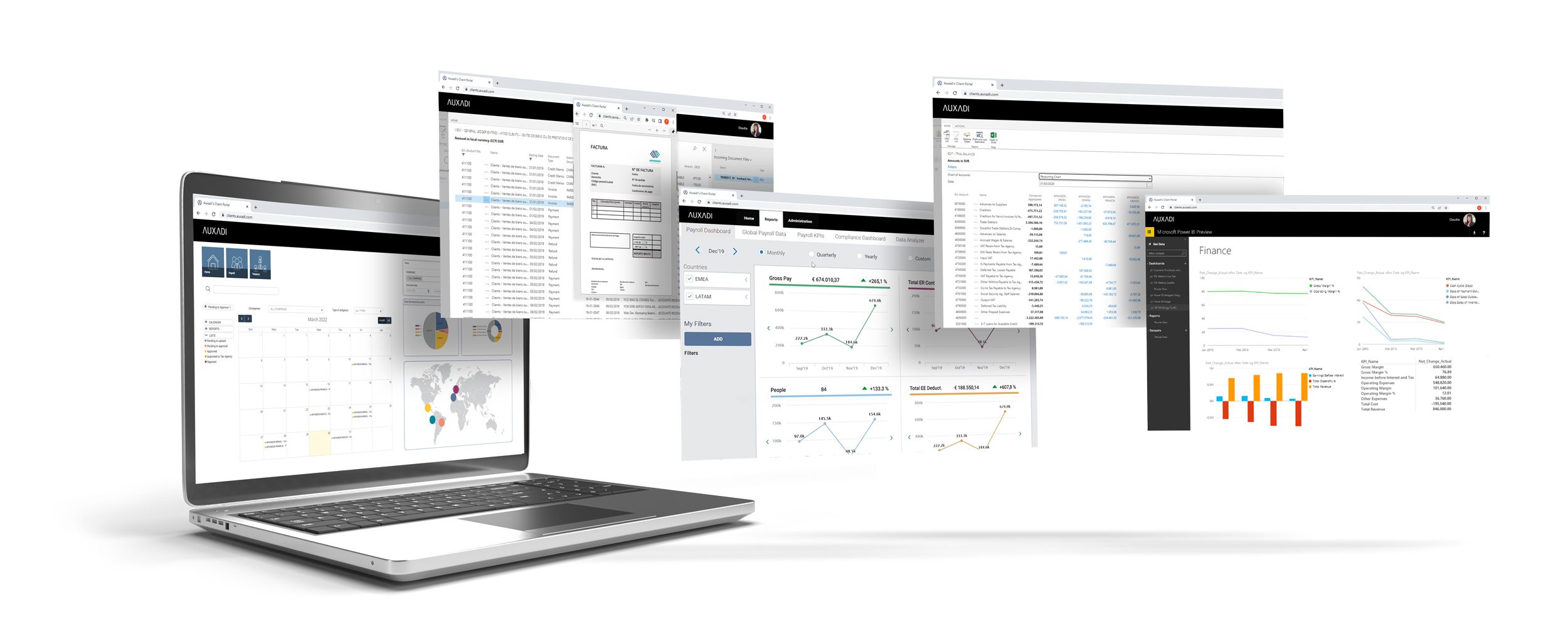
Here at Auxadi, we’ve used our 40+ years’ experience in what multinational companies need to design systems and processes to make your life easier. We’ve designed and developed a unique IT platform, built in partnership with Microsoft using NAV and Azure technologies. Our MySPV technology platform offers our clients data security, ease of access, homogenisation of country-specific terms, and real-time visibility.
With Auxadi managing your accounting, tax and payroll functions, there’s:
- No need to hire, train or provide space – as a third-party provider, we’ll operate independently.
- No financial outlay for staff or IT systems and no training downtime.
- No need for your finance or HR teams to learn new labour codes or tax laws – our local teams in 22 countries have all the expertise you need.
- No need to worry about your local accounting or reporting, bar a final check.
- We can grow with you in the future, providing services in locations as and when you need them, with no local recruitment headaches.
- With our industry-leading MySPV technology platform, you’ll have real-time cloud-based access to all your local accounts, tax and payroll, wherever and whenever you need it.
- Direct oversight – you will have real-time access to your data and real-time approvals.
- Single point of contact – you’ll have one person managing the team working on your account.
- No time zone issues: our International Desks are hard at work in the same hours you work.
Using our MultiCountry platform, you can login through the cloud and have immediate and real-time access to your accounts, your reports, and data from all of your international entities in one place. Everything you need is at your fingertips, any time of the day, from any location. Accessible with a single login, your data is secure and clearly defined, easily consolidated, and ready when you need it.
What’s more, we build reports to your specifications and they’re available with up-to-date figures whenever you need them.
You have visibility.
Our intuitive and secure platform allows you to approve payments, check your accounting reports, review the supporting documentation of line entries (invoices, bank statements, etc.), review your tax returns, raise invoices to your clients, and so much more – all through a single, easy-to-use portal.
You even have the option to connect to your existing systems, and there’s a complete set of additional functionalities and plug-ins which act together to provide you with the best, most robust, secure financial platform to manage your international business.
You have control.
Robotics, AI and Automation:
R&CA – drivers to boost your international expansion
New technologies are changing the way we relate to each other, the way we behave and, therefore, the way business is conducted. This is particularly relevant when it comes to international expansion.
New technologies make it possible to overcome the challenges and difficulties inherent in these processes, like geographic distance and different time zones. Technology also offers strategic opportunities for efficiency and productivity. And, more specifically, the application of Robotics and Cognitive Automation (R&CA) technologies can provide a competitive advantage when it comes to internationalisation. Let’s look at how.
A brief explanation to start. By robotics we mean the automation of tasks without any human rationality or cognition involved in the process – like step-by-step tasks. Cognitive Automation means automation of tasks that involve a certain rationality or replication of human intelligence.
Contrary to popular belief, the application of R&CA technologies will have more impact the further we advance up the organisation chart and through the complexity of different functions. As McKinsey states, “while less than five per cent of all occupations can be fully automated using technologies, about 60 percent of all occupations have at least 30 per cent of constituent activities that could be automated.”

What uses, applications and benefits can R&CA technologies bring to your internationalisation process?
- Standardisation of processes
- Execution of step-by-step tasks
- Automated decision making based on exponential volumes of information
- Support in the phases of documentation, research, admin processes and due diligence
- Obtaining insights – analysing collated data can prove invaluable
- Adaptability to peaks in transaction activity

These technologies have a transformational impact on organisations, including:
- Re-engineering processes – turning professionals into transformation leaders
- Promotion of analytical skills and new competencies, adding more value and contributing to the personal development of your teams
- Leveraging inter-generational diversity to promote learning
- Creating fast-growing experiences and/or career paths
- Using technology to transform job descriptions (complex judgements, soft skills)
- Transforms the vertical hierarchy into a system of self-managed teams

And, what should you consider when applying R&CA technologies to your international expansion process?
- Collaboration between Finance and IT departments is essential, particularly between the CFO and CTO. Therefore, it is a process in which organisational leaders and C-Suite profiles specifically must be involved
- These technologies don’t negate the need for human capital, but rather ensure that the talent you have is in a better position to apply strategic and added value
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement – the application is just the beginning. Having R&CA technologies also implies a culture of constant improvement, learning and innovation
- Technology is an ally of the international expansion process, bringing cybersecurity, efficiency, productivity, talent development, and many more benefits
Disruptive technologies like R&CA, AI, and machine-learning present significant opportunities for businesses looking to expand internationally, and will only present even more in the future – as they will not only automate certain tasks and activities but will provide greater operational resilience and help position your business for scalability and growth.
While significant opportunities are afforded by new technologies, it’s worth considering outsourcing any non-core activities to a third-party partner. External providers, like Auxadi, are investing heavily in technology and many have best-in-class systems in place to tackle your pain points and strategically enhance your operations so that you can focus on your global expansion, without significant financial outlay or training downtime.
Data privacy and security
Data is everything and must be fiercely protected. 54% of respondents in our International Expansion survey noted data protection and privacy to be the greatest concern for international expansion – while 38% of respondents noted that implementing data protection and privacy controls is their biggest concern.
Everyone is aware that there are data privacy and security laws and regulations in place to manage and control data storage, data use and data access. But, as everyone in international business knows, transferring data from your subsidiaries to your Head Office is also essential – so navigating and applying data privacy and security regulations is a key part of any international organisation.
Disruptive technologies like R&CA, AI, and machine-learning present significant opportunities for businesses looking to expand internationally
Every country in the world has specific data handling laws which cover everything from registrations and specifications on the role of Data Protection Officer, to how data is collected and processed, electronic marketing, online security and – what we’ll be looking at here – transferring data to other jurisdictions.
In this section, we’ll give an oversight of some of these data privacy and security regulations, how they’re enforced and the consequences of breaking them.
GDPR
When it comes to transferring data, GDPR states in Article 44 that transfers of personal data by a controller or processor to third countries outside the EU are permitted where GDPR conditions are met. Meaning, the third country recipient must have ‘adequate’ levels of data protection, as decided by the European Commission. The only countries/territories currently enjoying this approved adequacy: Andorra, Argentina, Canada (with exceptions), Faroe Islands, Guernsey, Israel, Isle of Man, Japan, Jersey, New Zealand, Switzerland, the United Kingdom and the Eastern Republic of Uruguay (EU added the UK to its list of ‘adequate’ countries in June 2021).
However, data transfers are also permitted where appropriate safeguards have been provided, and on the condition that there are enforceable data subject rights and effectively legal remedies available – and the list of appropriate safeguards includes (among others) binding corporate rules and standard contractual clauses. [It’s important to note that the EU-US Privacy Shield Framework is NOT considered an appropriate safeguard, as it was invalidated in 2020 (Case C311/18 of the European Court of Justice, 16 July 2020).]
The GDPR also includes a list of context-specific reasons for permitted transfers to third countries, though rules for Data Protection Officers, Data Supervisors, Data Controllers and Data Processors must be met or you risk fines.
All in all, GDPR and its Member State derivatives are intricate and technical. It’s recommended all businesses check with their lawyer as to the legality of data transfers.
Sector and state specific
The U.S. has several sector-specific national privacy or data security laws, applicable to financial institutions, telecoms companies, personal health information, credit report information, telemarketing and direct marketing.
However, the U.S. also has hundreds of relevant privacy or data security laws among its states and territories. These include requirements for: safeguarding, disposal, privacy policies, appropriate use of Social Security numbers, and data breach notifications. California alone has more than 25 separate privacy and data security laws.
In addition, The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has jurisdiction over a wide range of commercial sectors through its authority to prevent and protect consumers from unfair or deceptive trade practices, which include materially unfair privacy and data security practices. The FTC issues regulations enforces certain privacy laws, and takes action against companies who:
- Fail to implement reasonable data security measures
- Make materially inaccurate privacy and security representations, including in privacy policies
- Fail to abide by applicable industry self-regulatory principles
- Transfer (or attempt to transfer) personal information to an acquiring entity in a bankruptcy or M&A transaction, in a manner not expressly disclosed on the applicable consumer privacy policy
- Violate consumer privacy rights by collecting, using, sharing or failing to adequately protect consumer information, in violation of the FTC’s consumer privacy framework or certain national privacy laws and regulations.
The Attorneys General of many states have similar enforcement authority to the FTC.
Even though no geographic transfer restrictions apply in the U.S., except with regard to storing some governmental records and information – we recommend you definitely seek local guidance if you’re importing or exporting data to the U.S.
LGPD
The Brazilian General Data Protection Law (LGPD) [Federal Law no. 13,709/2018] has been in force since September 2020, but penalties were not enforceable until August 2021, giving businesses a grace period to improve their procedures and systems. The LGPD is Brazil’s first comprehensive data protection regulation and it’s generally aligned to GDPR.
The LGPD applies to any processing operation carried out by a natural person or a legal entity, of public or private law – irrespective of the means used for the processing, the country in which its headquarters is located, or the country where the data are located – provided that:
- The processing operation is carried out in Brazil;
- The purpose of the processing activity is to offer or provide goods or services, or the processing of data of individuals located in Brazil;
- The personal data was collected in Brazil.
When it comes to data transfers, like GDPR, Brazil requires that the LGPD is complied with and prior specific and informed consent gained, unless:
- The transfer is to countries or international organisations with an adequate level of protection of personal data;
- There are adequate guarantees of compliance with the principles and rights of data subject provided by LGPD, in the form of:
- Specific contractual clauses for a given transfer
- Standard contractual clauses
- Global corporate norms
- Regularly issued stamps, certificates and codes of conduct;
- The transfer is necessary for international legal cooperation between public intelligence, investigative, and prosecutorial agencies;
- The transfer is necessary to protect life or physical safety of the data subject, or of a third party;
- Authorisation has been provided by the National Data Protection Authority (ANPD);
- The transfer is subject to a commitment undertaken through international cooperation;
- The transfer is necessary for the execution of a public policy or legal attribution of public service;
- The transfer is necessary for compliance with a legal or regulatory obligation, execution of a contract or preliminary procedures related to a contract, or the regular exercise of rights in judicial, administrative or arbitration procedures.
As with GDPR, it’s recommended you get legal advice before transferring data to or from Brazil.
Federal Law on protection of personal data
The Federal Law on the Protection of Personal Data held by Private Parties (Ley Federal de Protección de Datos Personales en Posesión de los Particulares) (“the Law”) entered into force on 6 July 2010. This regulation was followed by seven other directives from 2011 to 2018, all of which delve further into Data Protection specificities.
Essentially, regulations apply to all processing of personal data when:
- Processed in a facility of the data controller located in Mexican territory;
- Processed by a data processor, regardless of location, if the processing is performed on behalf of a Mexican data controller;
- Where Mexican legislation is applicable as a consequence of Mexico’s adherence to an international convention or the execution of a contract (even where the data controller is not located in Mexico);
- Where the data controller is not located in Mexican territory, but uses means located in Mexico to process personal data, unless such means are used only for transit purposes.
The Law only applies to private individuals or legal entities that process personal data, and not to the government, credit reporting companies governed by the Law Regulating Credit Reporting Companies, or persons carrying out the collection and storage of personal data exclusively for personal use (and not disclosed for commercial use).
Regarding data transfers, where the data controller intends to transfer personal data to domestic or foreign third parties other than the data processor, it must provide the third parties with the Privacy Notice provided to the data subject and detail the purposes to which the data subject has limited and specified. Processing by the third-party must be consistent with what was agreed in the Privacy Notice, which shall contain a clause indicating whether or not the data subject agrees to the transfer of their data. The third-party recipient assumes the same obligations as the data controller who has transferred the data.
However, domestic or international transfers of personal data may be carried out without the consent of the data subject where the transfer is:
- Pursuant to a law or treaty to which Mexico is party;
- Necessary for medical diagnosis or prevention, health care delivery, medical treatment or health services management;
- Made to the holding company, subsidiaries, or affiliates under the common control of the data controller, or to a parent company (or any company of the same group) of the data controller, operating under the same internal processes and policies as the data controller;
- Necessary by virtue of an executed contract between the data controller and a third party in the interest of the data subject;
- Necessary or legally required to safeguard public interest or for the administration of justice;
- Necessary for the recognition, exercise or defence of a right in a judicial proceeding;
- Necessary to maintain or comply with an obligation resulting from a legal relationship between the data controller and the data subject.
The Regulations state that the data subject doesn’t need to be informed or consent to communications or transmissions of personal data to data processors. However, the data processor must do all of the following:
- Process personal data only according to the instructions of the data controller;
- Not process personal data for a purpose other than as instructed by the data controller;
- Implement the security measures required by the Law, the Regulations and other applicable laws and regulations;
- Maintain the confidentiality of the personal data subject to processing;
- Delete personal data processed after the legal relationship with the data controller ends or when instructed by the data controller, unless there is a legal requirement for the preservation of the personal data;
- Not transfer personal data unless instructed by the data controller, the communication arises from subcontracting, or if required by a competent authority.
It’s recommended you seek advice from legal partners before transferring data to or from Mexico.
UK GDPR
As part of the EU, the UK originally enforced the EU’s GDPR laws. Post-Brexit, the UK Government has transposed GDPR into UK national law – creating UK GDPR in early 2021. Though the law has a number of technical differences to the original, the material obligations of data controllers and processors are essentially the same as Europe’s version.
Supplementing UK GDPR is the Data Protection Act 2018 (DPA), which deals with some matters exempt from EU GDPR, and merging some other EU regulations into UK law. For example, Part 3 of the DPA covers EU Law Enforcement Directive (EU2016/680), creating a regime specifically for personal data processing by law enforcement.
UK GDPR, like its cousin, applies to any organisation that processes personal data of data subjects within the United Kingdom, including “offering goods and services” and “monitoring of their behaviour”.
When it comes to data transfers, the UK Government has the power to make an adequacy decision – involving the UK Secretary of State determining that the third country provides an adequate level of data protection and personal data may be freely transferred. The countries currently on the list have been rolled directly from the EU version, and the UK treats all EU and European Economic Area Member States as adequate – at least for the moment. All these adequacy decisions will be reassessed before the end of 2024.
There’s also a list of appropriate safeguards to permit data transfers to third countries, just like EU GDPR, and DPA Schedule 21 allows EU Commission approved standard contractual clauses to continue to be used for transfers under the UK GDPR, until they replaced by clauses issued by the UK Government.
Blockchain
Gaining popularity thanks to crypto-currencies, a blockchain is defined as a decentralised database logging an unlimited number of data assets and transactions through a peer-to-peer network. It’s essentially a registry maintained by a consensus algorithm and stored in a network of “nodes” – computers that allow data to be included in “blocks” that are connected (chained) one to another.
Blockchain databases may be deployed in many circumstances and scenarios, including within the financial services and insurance sectors for money transfers, securities transfers and lending.
The advantages of blockchain include, amongst others; transparent and tamper-proof processes, disintermediation and cost reductions, security (because of the chaining process), and an additional layer of trust due to the fact that each transaction is verified by a wider audience of “nodes”.
Regulators are setting up legal frameworks for operating a blockchains, but many are yet to be finalised. The relationship between blockchain (and other distributed ledger technologies, or DLTs) and personal data protection has yet to be fully addressed.
The decentralised nature of blockchains (where data is held on a series of nodes instead of in a single location), means that it doesn’t generally adhere to regulations which focus on a ‘centralised’ approach to data processing, like GDPR. This decentralisation makes it difficult to identify the data controllers, i.e. the entity determining the means and purposes of data processing.
In addition to the practical difficulties in effectively identifying the nodes to which to submit the data request, certain rights of the data subject can be affected. For example, under GDPR, the principle of data minimisation provides that data must be processed for specified and explicit purposes and only for the time strictly necessary for the processing. In most cases, however, data added to a blockchain will remain stored in perpetuity as part of an append-only database.
This also affects other GDPR rights, like the right of amendment and rectification, and the right to be forgotten – as it’s almost impossible to erase or adjust the data after it’s entered due to blockchain’s essential decentralised nature. While this security feature of blockchains may seem appealing, it does essentially go against many data protection regulations.
Regulators are, therefore, facing the challenge of protecting the fundamental rights of the individual, while not affecting the technology and innovation.
As regulators operate on their own timetables, we advise careful assessment and legal advice when using blockchain-based technologies and databases.
The advantages of blockchain include, amongst others; transparent and tamper-proof processes, disintermediation and cost reductions, security (because of the chaining process), and an additional layer of trust due to the fact that each transaction is verified by a wider audience of “nodes”
Seek guidance from knowledgeable partners
It’s highly recommended that all businesses take a firm stance on data privacy and security. It’s a serious subject and requires serious protections for both client and company data. In our hyper-connected world, and at a time when more and more businesses and individuals are entrusting personal data to cloud services, data breaches are an unfortunate regular occurrence and must be contained.
Knowing the right local experts and advisers on the ground is crucial to ensuring you have the right data privacy and security measures in place, ensuring your international compliance, so you won’t fall foul of any potential reputational and/or regulatory consequences.
Digital transformation and taxation
Looking closer at the digitisation of business, the functions of tax management and regulatory compliance are probably most exposed to (and, to a great extent, receive the most benefits from) digital transformation, particularly for international companies. Though digital transformations are underway in many countries, the COVID-19 pandemic catalysed administrations and underlined the importance of having a digitised tax system – particularly in relation to internationalisation and cross-border operations.
Digital transformation has special implications when it comes to companies in the process of international expansion or managing activity in multiple jurisdictions. This trend for digitisation has already seen special relevance in everything related to transfer pricing – the intense activity shown by different international regulators is forcing finance directors and tax departments to automate and harmonise transfer pricing management at the group level, guaranteeing cross-border compliance.
But innovation doesn’t end here. Tax administrations are also advancing their use of Big Data and analytics to automate their financial functions, grow in efficiency, and be able to automatically detect possible breaches or areas of improvement.
Many different countries (with difference economic classifications) have already launched initiatives for taxation and digital transformation. As stated by CIAT, the United Kingdom has launched the Connect system that facilitates data mining to detect fraudulent activities; Australia is developing ANGIE, which will automatically identify relationships between taxpayers; while the Canadian CRA uses data analysis to combat tax evasion abroad.
What’s the response of organisations and CFOs?
New technologies are presenting solutions which, just a short while ago, seemed unthinkable. For example, the application of data analytics and machine learning are allowing CFOs to obtain and analyse large amounts of information (both vertically and transversally throughout the organisation) to establish predictions and implement strategic decisions. The implementation of Robotic & Cognitive Automation (R&CA) technologies offers distinct advantages, like process automation, resource scalability, and an improvement in ROI in strategic management. Blockchain technology is simplifying all those processes which, until now, had their basis in trust, such as due diligence or the signing of contracts, among many others.

This situation, and the very context of digital transformation, presents challenges for the CFO. You should consider:
- Aligning the company with the purpose of digital transformation, to ensure that the digitalisation process is global and coordinated, and not only applied to the tax function.
- Responding to the technological and regulatory compliance needs resulting from operating in an international context; providing a solution to the needs of each country or jurisdiction in which you operate, in a coordinated and homogeneous manner.
- Evolving your role from leader of the finance function to leader of digitalisation, strategic data analysis, or change, among others.
- Ensuring transparency and complete availability of information.
- Ensuring that your organisation is ready to respond to the technological challenges of today, but especially those of tomorrow.
Tax automation
At Auxadi, we have our own purpose-built MySPV technology platform, which allows us to monitor the obligations of our clients in real-time and keep them correctly archived – providing agility, establishing control processes, avoiding duplication of tasks and reducing the presence of errors.
Our tax automation tool allows us to monitor our client’s obligations accurately while saving them countless hours of manual work – allowing their teams to focus on more value-add tasks. We’ll also ensure regulatory compliance in different jurisdictions and give you the strongest guarantee of confidentiality and data security.
Copyright 2022 Auxadi Contables & Consultores, S.A. | All rights reserved
Legal notice | Privacy and Data Protection Policy | Cookies Policy